Ibuprofen is in a group of medicines known as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
It's used to treat different types of pain such as headache, migraine, dental pain, back pain or muscle pain, and pain from injury. Read more about pain and pain relief medication. It also helps to ease redness and swelling, and to treat fever.
Low or no data? Visit zero.govt.nz, scroll down the page then click on our logo to return to our site and browse for free.
Ibuprofen for adults
Sounds like 'eye-bew-pro-fen'
Key points about ibuprofen
- Ibuprofen is used to treat pain, inflammation and fever.
- Ibuprofen is in a group of medicines known as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Find out how to take it safely and possible side effects.
- Note: the information on this page is about ibuprofen for adults. For information about use for children, see ibuprofen for children.
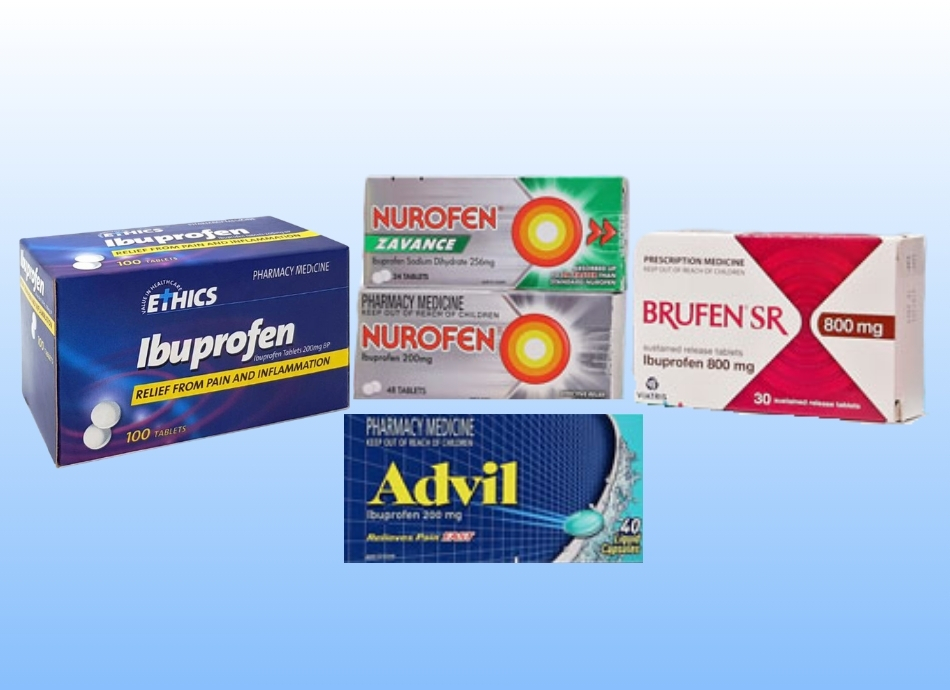
| Ibuprofen is known by different brand names, for example: | |
|
|
| Ibuprofen is also contained in some other combination medications such as: | |
|
|
The lower strength (200 mg) tablets can be bought from a supermarket or over-the-counter from a pharmacy. The higher strength tablets (400 mg, 800 mg) tablets are only available on prescription from your doctor.
The dose of ibuprofen will be different for different people depending on your condition and which strength of medicine you are taking.
- The usual dose for adults is 200 mg to 400 mg 3 or 4 times daily if needed.
- Take the lowest dose for the shortest time. Usually, you should only need to take ibuprofen for a short time eg, while you have pain or swelling. Use the lowest dose that works for you and stop as soon as you can. Don't take more than the recommended amount which is usually 1200 mg daily. High doses can be harmful.
- Always follow the directions on the package or pharmacy label. If you don't know how much to take, check with your pharmacist.
- Take ibuprofen with a full glass of water and stay hydrated while taking ibuprofen to protect your kidneys. Swallow the tablets whole, don't crush or chew them.
- If ibuprofen causes a stomach upset, take it with or just after food.
- Limit or avoid alcohol while you are taking ibuprofen. Alcohol can increase the risk of side effects like stomach upset.
- Missed dose: If you forget to take a dose, take it when you next need pain relief and then continue as before. Don't take 2 doses together to make up for a missed dose.
For most people taking ibuprofen is safe but extra care is needed in some situations, for example if:
- you have high blood pressure
- you have heart or kidney problems or asthma
- you're aged 65 years or older
- you smoke.
It can be harmful if you take ibuprofen when you are dehydrated or have been sick with diarrhoea (runny poos) or vomiting. Read more about the risks of NSAIDs.
| When you should NOT take ibuprofen |
|
Ibuprofen should NOT be used in some situations as it can be harmful.
Read more about the risks associated with NSAIDs. |
Ibuprofen is found in many pain medicines you can buy from the pharmacy such as Nurofen Plus® and Maxigesic®.
Serious side effects can happen if you take more than one ibuprofen-containing medicine. If you do take other medicines that have ibuprofen in them, be careful not to take more than the recommended dose of ibuprofen each day which is usually 1200 mg.
Do not take other anti-inflammatory medicines such as diclofenac, naproxen or celecoxib while taking ibuprofen. This can increase your risk of side effects.
It's safe to take ibuprofen with paracetamol because they work differently.
Ibuprofen interacts with some medicines, especially those used for high blood pressure, so check with your doctor or pharmacist before you start taking ibuprofen.
Image credit: University of Otago, NZ
Taking NSAIDs together with blood pressure medicines can be harmful to your kidneys. This is called the ‘triple whammy’. If you are taking blood pressure medicines (ACE inhibitors or ARBs and diuretics) tell your doctor or pharmacist before starting ibuprofen.
- Examples of ACE inhibitors are captopril, cilazapril, enalapril, lisinopril, perindopril and quinapril.
- Examples of ARBs are candesartan, irbesartan and losartan.
- Examples of diuretics are furosemide, bumetanide, bendroflumethiazide, chlortalidone, indapamide, spironolactone, eplerenone and metolazone.
Read more about the triple whammy.(external link)
| Side effects | What should I do? |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Did you know that you can report a side effect to a medicine to CARM (Centre for Adverse Reactions Monitoring)? Report a side effect to a product.(external link) | |
The following links provide further information about ibuprofen. Be aware that websites from other countries may have information that differs from NZ recommendations.
Ibuprofen(external link) (Māori(external link)) NZ Formulary Patient Information, NZ
Ibuprofen for pain and inflammation(external link) Patient info, UK
Ibuprofen patient information guide(external link) SafeRx, Waitematā DHB, NZ
Resources
5 questions to ask about your medications(external link) Health Quality and Safety Commission, NZ, 2019 English(external link)(external link)(external link), te reo Māori(external link)(external link)(external link)
References
- Ibuprofen and cardiovascular safety(external link) Medsafe Safety Information, NZ June 2015
- Ibuprofen(external link) NZ Formulary, NZ, May 2022
Brochures

Healthify He Puna Waiora, NZ, 2022
EnglishTe reo Māori
Samoan
Tongan
Chinese (simplified)
Cook Islands Māori
My Medicines, NZ, 2018
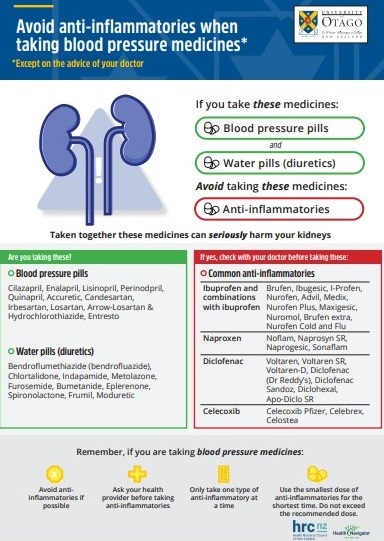
University of Otago, NZ, 2021
Credits: Sandra Ponen, Pharmacist, Healthify He Puna Waiora. Healthify is brought to you by Health Navigator Charitable Trust.
Reviewed by: Angela Lambie, Pharmacist, Auckland
Last reviewed:
Page last updated:





