An ear infection is the most common cause of ear pain. The infection often begins as a cold, flu, sinus infection or throat infection and spreads to the middle ear (otitis media) where it causes ear pain and often fever.
Other causes include:
- Earwax build-up or blockage – a piece of hard earwax can cause ear pain or discomfort. If the earwax is pushed deeper by cotton buds, the ear canal can become blocked and cause more pain. Read more about earwax build-up and removal.
- Swimmer's ear – frequent swimming can cause an infection or irritation in your outer ear because of water that remains in your ear canal. This can cause pain and itching in your ear. Read more about swimmer's ear.
- Injury to your ear canal – a fingernail, cotton bud or any other object can cause injury to your ear canal causing ear pain.
- An object in the ear canal – young children may put small objects in their ear canal. It can cause pain, especially if the object is sharp or pushed in a long way.
- Abscess in your ear canal – an infection of a hair follicle in the ear canal can be very painful. It looks like a small red bump, and sometimes turns into a pimple.
- Airplane ear – if the ear canal is blocked, sudden increases in air pressure can cause the eardrum to stretch, resulting in severe ear pain. This usually happens during air travel, when the plane is coming down for landing, or when driving at high altitudes.
- Referred pain – referred pain is felt in your ear but is due to something that is not in your ear, such as a tonsil infection, tooth decay or mumps.
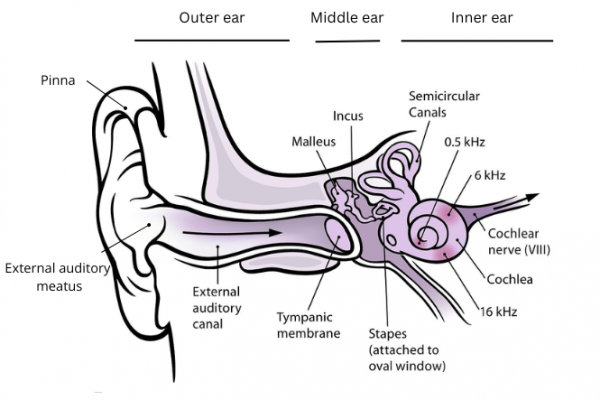
Image credit: Wikimedia Commons







