Budesonide and formoterol are 2 medicines mixed together in a single inhaler device such as a turbuhaler or a metered dose inhaler (MDI or puffer). The combination is used to treat the symptoms of asthma and COPD and to prevent them from recurring.
- Budesonide is a corticosteroid and when inhaled works by preventing swelling and irritation in the walls of the small air passages in your lungs. It is also called a preventer because when used every day it prevents asthma attacks.
- Formoterol is a long-acting, fast onset bronchodilator and works by relaxing and opening up your air passages, making breathing easier.
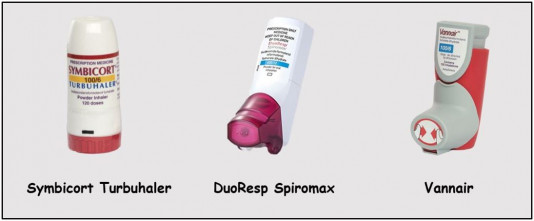
In New Zealand, budesonide + formoterol inhalers are available in different brands, inhaler devices and strengths.
- Symbicort: A dry powder inhaler that is in a turbuhaler device.
- DuoResp Spiromax: A dry powder inhaler that looks like a metered dose inhaler.
- Vannair: A metered dose inhaler (MDI or puffer).
Using an inhaler device enables the medicine to go straight into your airways when you breathe in. This means that your airways and lungs are treated, but very little of the medicine gets into the rest of your body.
Read more about the different inhaler devices and deciding on the right inhaler for you.
For more detailed information on the different brands of budesonide + formoterol, click on the following links:









