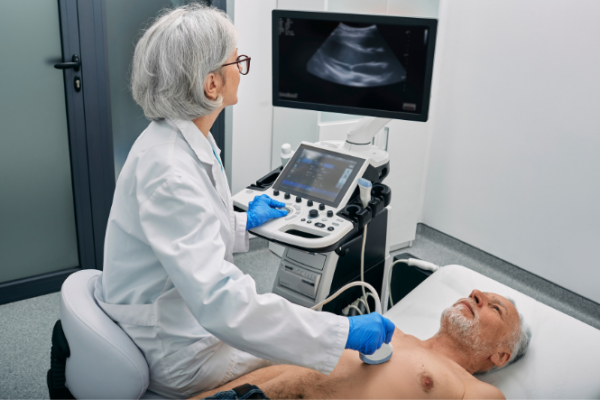
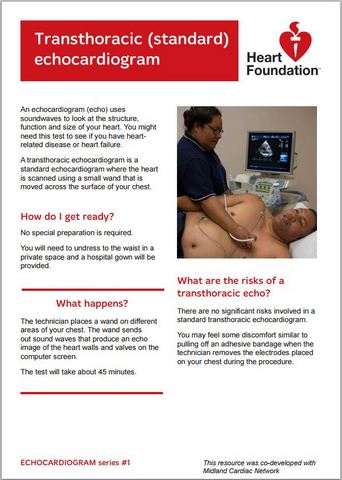
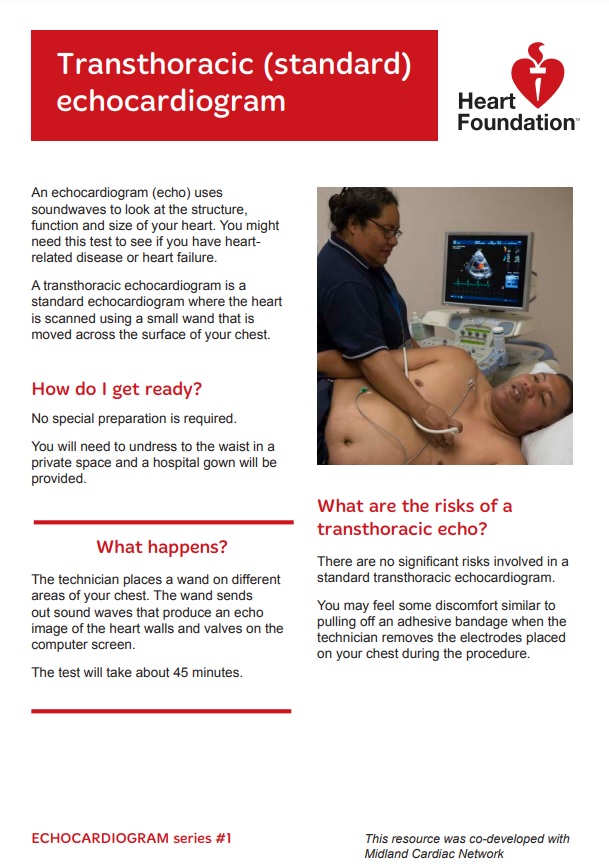
Sometimes the transthoracic or standard echo doesn't provide enough information and your doctor may request a more specialised echo test.
Exercise stress echocardiogram
During this type of echo you'll be asked to walk on a treadmill or ride an exercise bike while pictures are taken of your heart. This allows your doctor to understand how your heart copes when it's made to work harder, and is helpful to diagnose whether you have angina or not. It can also give your doctor information about the severity of a heart-valve problem.
Dobutamine stress echocardiogram
This type of echo also allows your doctor to understand how your heart copes when it's made to work harder. If you can't exercise, you may be given medicine called dobutamine to make your heart react as if you were exercising. A drip will be put in a vein in your arm, and dobutamine will be infused into the drip, causing your heart to work harder. While this is happening, the technician will take pictures of your heart using an ultrasound probe gently placed on your chest.
Sometimes an even more specialised echocardiogram might be needed, see the section below.