Blockage in the wall of your heart arteries (coronary arteries) is caused by the build-up of plaques. These plaques mostly contain fats, cholesterol and calcium deposits and the build-up is often called hardening of the arteries. Plaques can grow gradually over time and block the blood flow to your heart muscle. This can cause symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, a heart attack or other heart problems.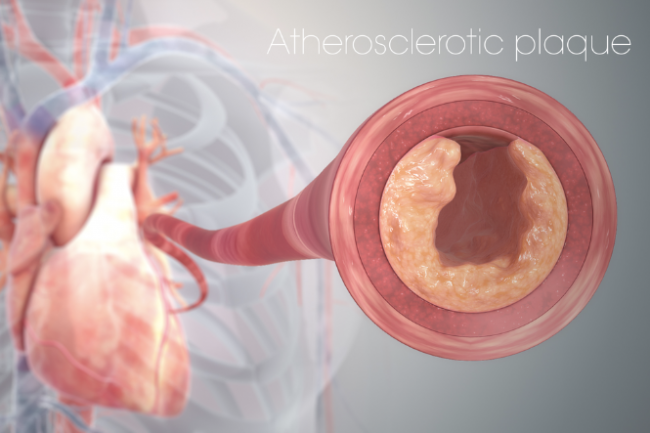
Image credit: Scientific Animation Wikimedia Commons
Low or no data? Visit zero.govt.nz, scroll down the page then click on our logo to return to our site and browse for free.
CT calcium score
Also known as computed tomographic (CT) calcium score or coronary artery calcium scoring
Key points about CT calcium score
- A CT calcium score test uses X-rays during a CT scan of your heart to detect calcium deposits in the plaques (sounds like plarks) which can build up in the arteries of your heart (coronary arteries).

A CT calcium score test uses X-rays to scan your heart to detect calcium deposits in the plaques that can build up in the arteries of your heart (coronary arteries). By detecting the amount of calcium deposited in your coronary arteries using a CT scanner, it can then provide a calcium score. The more calcium in your coronary arteries, the higher your risk of heart disease.
A CT calcium score test is one way to assess your risk of heart disease. It is usually done to detect any blockage in your heart arteries before you have any symptoms of heart attack or heart disease. The results of the test will help your healthcare providers advise you about any need for medication or lifestyle changes to reduce your chances of having heart problems.
Risk factors for heart disease include things that you can't change (eg, your age, biological sex and family history) and factors that you can change. These include:
- smoking
- high blood glucose levels with diabetes
- high blood pressure
- high cholesterol levels
- increased weight
- reduced physical activity
- high alcohol consumption.
Read more about risk factors for heart disease and heart risk assessment.
CT calcium score testing is only available through the public health system in some areas. If you would like to know about the state of your coronary arteries, talk to your healthcare provider to find out whether the CT calcium score test is suitable for you. Also check what the cost will be if you go privately (pay for it yourself).
If you have any heart symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, reduced exercise tolerance or palpitations, your doctor may recommend other tests, eg, an electrocardiogram (ECG), exercise stress test or echocardiogram.
Read more about heart disease tests.
Similar to a CT scan, you will need to lie flat on a bed while it moves through the CT scanner which is large and round like a doughnut.
The scan will be of better quality if your heart rate is below 60 beats per minute. Your doctor may ask you to take a tablet, eg, metoprolol to slow down your heart rate before the procedure. It is also recommended that you avoid tea or coffee or stressful situations before the procedure to prevent your heart from racing.
The CT calcium score test involves only a small amount of radiation and is considered very safe. It doesn't require any injections or dye.
The result of the test is given as an Agatston score ranging from 0–1000. This is calculated based on the amount or volume of calcium detected in your coronary arteries. The more calcium build up you have, the higher the score. A higher score means your risk of getting heart disease is greater. Your healthcare provider will consider your other heart risk factors, and may suggest you have further tests or make changes to reduce their impact.
Read more about risk factors for heart disease and heart risk assessment.
Talk to your doctor if you are unsure about your CT calcium score test result or if you are concerned about your heart health.
Resources
Brochures
Apps/tools
References
- Heart scan (coronary calcium scan)(external link)(external link)(external link) Mayo Clinic, US
- Calcium-score screening heart scan(external link)(external link)(external link) Cleveland Clinic, US
Information for healthcare providers
Webinar – New NZ CVD primary care 2018 guidelines(external link)(external link)(external link) Goodfellow Unit, NZ
Credits: Healthify editorial team. Healthify is brought to you by Health Navigator Charitable Trust.
Reviewed by: Associate Professor Sue Wells, Public Health Physician, University of Auckland
Last reviewed:
Page last updated:





